syifbhuiyan
Automated Sentiment & Theme Extraction from Social Media
Goal: To build a reusable Natural Language Processing (NLP) pipeline that cleans unstructured text, quantifies emotional valence, and discovers hidden thematic structures without human supervision.
🛠 Tools Used
- Python (Pandas, NumPy)
- NLTK (Text Preprocessing & Lemmatization)
- VADER (Sentiment Analysis)
- Gensim (LDA Topic Modeling)
- Seaborn (Visualization)
📋 Project Overview
Social media platforms generate massive amounts of unstructured text data. For researchers and businesses, manually reading thousands of comments to gauge public opinion is impossible.
In this project, I developed a computational framework to “read” and categorize disparate social media comments. The pipeline moves from preprocessing (cleaning slang, removing stopwords) to inferential modeling (determining sentiment and topics). This methodology shifts textual data from purely qualitative to a quantitative resource suitable for statistical analysis.
🔍 Key Findings & Insights
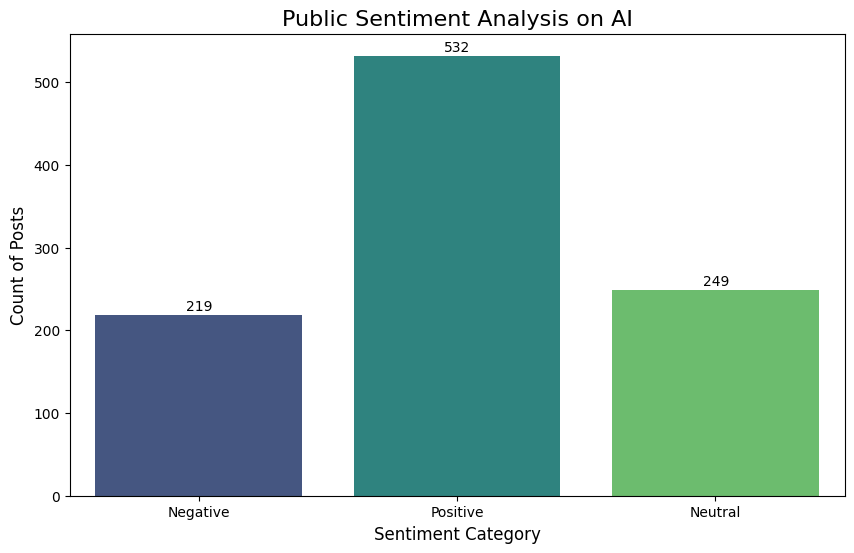
Applying the pipeline to a sample dataset of 1,000 public comments revealed distinct patterns in user discourse:
- Positive Dominance:
- The majority of the sampled discourse was Positive (53.2%), significantly outweighing Negative (21.9%) sentiment. This challenges the common assumption that social media is primarily a venue for negative venting.
- Thematic Clusters (LDA Results):
- Using Latent Dirichlet Allocation, the model successfully grouped the “messy” text into coherent topics without prior labeling:
- Cluster 1 (Celebration): Defined by terms like birthday, family, sunday, home.
- Cluster 2 (Connection): Defined by terms like love, people, healthy, model.
- Cluster 3 (Gratitude): Defined by terms like thankful, father, happy, good.
- Using Latent Dirichlet Allocation, the model successfully grouped the “messy” text into coherent topics without prior labeling:
📊 Visualizing the Impact
The chart below visualizes the sentiment distribution across the corpus, highlighting the skew toward positive engagement in this specific dataset.
💻 Code Snippet: The Cleaning Logic
Text data is notoriously noisy. Below is the custom function I wrote to normalize the text data for the machine learning models.
def refine_text(raw_text):
# Convert to string and lowercase
text = str(raw_text).lower()
# Remove technical artifacts (URLs, Usernames)
text = re.sub(r'http\S+|www\.\S+', '', text)
text = re.sub(r'@\w+', '', text)
# Lemmatize tokens (e.g., "running" -> "run")
# This requires tokenization and stopword lists loaded previously
cleaned_tokens = [lemmatizer.lemmatize(word) for word in tokens
if word not in stop_words and len(word) > 2]
return " ".join(cleaned_tokens)